Fabric cutting machines: how they work, types and applications
Fabric cutting machines offer suitable solutions for every production need, from small craft to large industrial production. The choice of machine can depend on many factors: the type of fabric to be processed, the complexity of the cuts required, the scale of production, and the specific needs for precision and speed. Continuous innovation in this field ensures that textile cutting technologies are constantly evolving, with the introduction of increasingly sophisticated and high-performance tools aimed at meeting the growing demands of the market. Technological development aimed not only at improving the quality and efficiency of cutting, but also at reducing production costs and environmental impact, making the textile industry increasingly sustainable and competitive.

Cutting machines: what they are and how they work
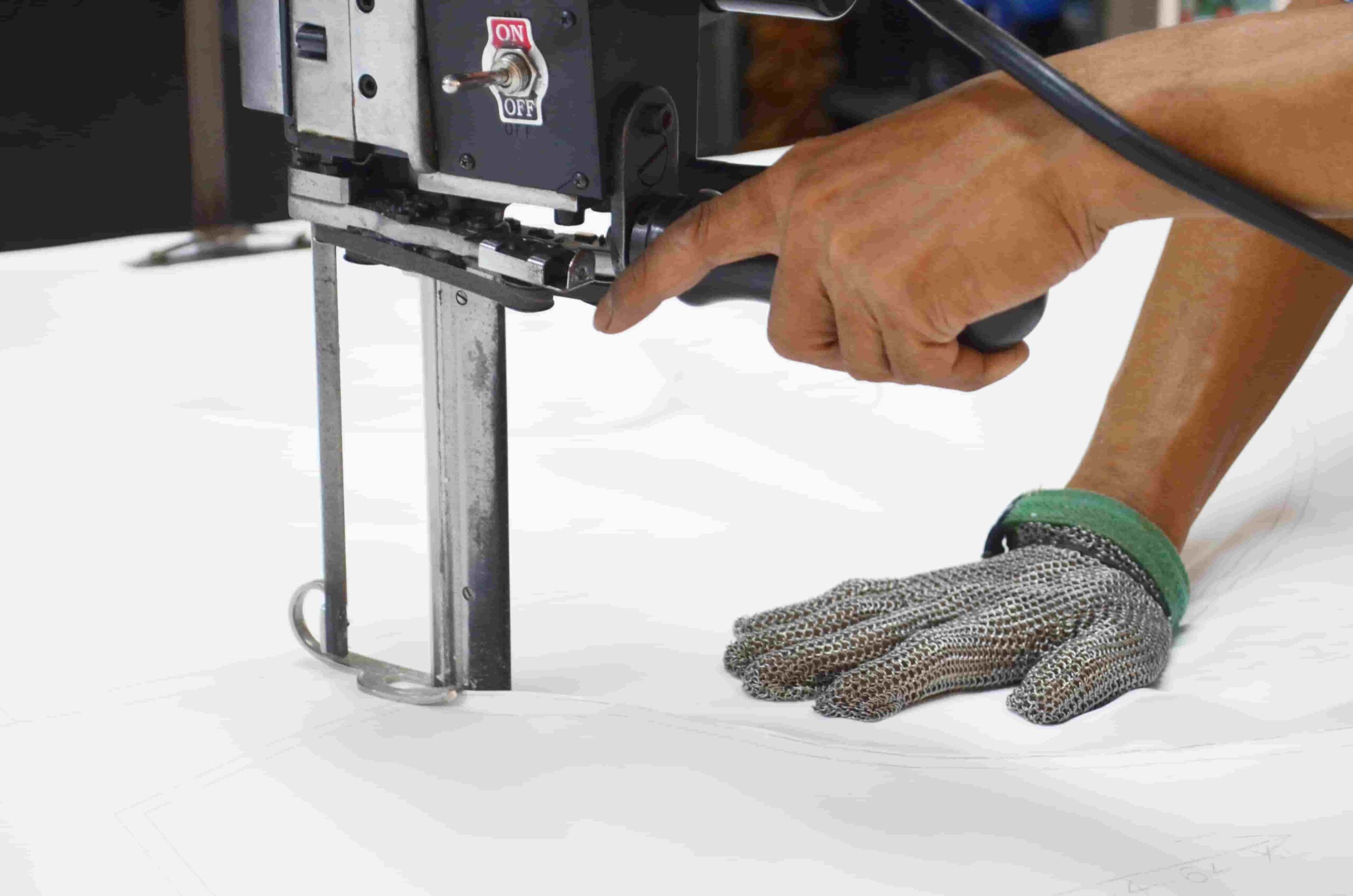
Textile cutting machines are key components in the textile industry because they enable precise and efficient processing of a wide range of textile materials. Different models range from simple manual cutters to sophisticated automated machines, each with specific features for different applications. For example, manual cutters, with fixed or rotating blades, allow operators to perform detailed, curved cuts typical of craft and small production work, while electric and automatic machines, equipped with high-efficiency motors and computerized control systems (CNC), allow complex cuts to be programmed and large volumes of fabric to be handled with pinpoint accuracy, optimizing workflow and reducing production time.
Types of fabric cutting machines
The cutting machine market offers a wide variety of solutions, each designed for specific applications, fabrics and different levels of precision, efficiency and versatility. Manual cutters are the most common and are the essential tools of the trade for small craft workshops because they allow linear and curved cuts with precise manual control. Rotary-blade models, on the other hand, allow deeper cutting through multiple layers of fabric, ensuring sharp edges and limiting additional trimming as much as possible.
An evolution of manuals, electric cutters are equipped with motors that power the blade, allowing less physical effort and increased cutting speed. Ideal for small and medium production runs, they allow the operator to maintain a steady work pace without fatigue.
Another relevant category is that of fixed-blade cutters, used mainly for straight and long cuts. These are machines that provide high precision on large fabrics, often assisted by guiding systems that ensure that the blade follows exactly the desired cutting line.
There are specialized machines such as vertical blade cutters, used primarily for straight cuts on heavy or layered fabrics. These tools have a vertical blade that moves up and down, cutting through the material with punctuality and force. They are commonly used for cutting stiff, dense fabrics, such as denim or waxed canvas, where a sharp, clean cut must be resorted to.
Ever-present in industrial settings, automated cutting machines have been (and still are) a real breakthrough in textile manufacturing processes. These machines, controlled by computerized numerical control (CNC) systems, allow complex cuts to be programmed with pinpoint accuracy.
More unique and specific for flawless finishes, waterjet cutters use a stream of water at very high pressure to cut fabrics without heating them, making them perfect for processing heat-sensitive technical and composite materials. Similarly, laser cutters employ laser beams to make intricate cuts and automatically seal the edges of synthetic fabrics, preventing fraying. Ultrasonic cutters, on the other hand, use high-frequency vibrations to etch fabrics, minimizing the risk of damage to delicate, lightweight materials that could be ruined by the heat or friction of conventional blades.
To make contoured and complex cuts on thick materials, resort to belt cutters, equipped with a continuous belt blade that moves vertically while maintaining constant tension, for detailed cuts even on multiple layers of fabric.
Moving table cutters combine table mobility with a fixed blade, optimizing precision when cutting on large pieces of fabric without the need for frequent repositioning of the material. This combination of mobility and precision is particularly useful in industrial settings where the key words are productivity and efficiency. Plotter cutters, controlled by CNC systems, are particularly valued for their ability to perform custom and highly complicated cuts typical of custom manufacturing and prototype developers. These devices use sharp blades that follow programmed paths with extreme precision, adapting to various types of fabrics and thicknesses.
Another innovation in the field of fabric cutting machines is digital cutters, which integrate advanced machine vision and artificial intelligence technologies to optimize cutting processes, as they can automatically detect defects in fabrics and adapt cutting paths in real time, improving the quality of the final product and reducing material waste.
Benefits in the textile industry
The use of advanced cutting machinery in the textile industry offers many advantages in terms of productivity, precision and quality of work, with more efficient and competitive processes. One of the main benefits is increased productivity. Automated cutting machines, such as computer numerical control (CNC) cutters, allow large quantities of fabric to be cut in less time than manual methods. This allows companies to fulfill large orders more quickly, optimizing workflow and reducing production time.
Precision is another crucial aspect resulting from the use of modern cutting machines. Laser, water-jet and ultrasonic cutting machines, for example, offer a level of precision that is difficult to achieve with manual cutting because they are equipped with technologies that allow complex and detailed cuts to be made with minimal margins of error, ensuring that each piece of fabric conforms to the required specifications. This precision is particularly important for the production of made-to-measure garments and for cutting technical fabrics used in industrial applications.
Also improving is the quality of the final product: the edges of fabrics cut with laser or ultrasonic technologies are often sealed automatically during the cutting process, preventing fraying and ensuring a clean, professional appearance. Consequently, operational efficiency also increased significantly by reducing material waste. Automated cutting machines are able to optimize fabric use by calculating the ideal placement of cuts to minimize waste. This results in reduced production costs and the adoption of a more sustainable approach geared toward minimizing the waste of valuable resources.
Another significant benefit is the reduction in physical fatigue and risk of injury to operators. Electric and automated cutters require less physical exertion than manual cutters, allowing operators to work for longer periods of time without overexerting themselves. In addition, automation of cutting processes reduces the risk of accidents related to the use of sharp blades, improving safety standards at workstations.
Industrial (and other) Applications
Fabric cutting machines find applications in a wide range of industries due to their versatility and precision. In industry, one of the main applications is in apparel and fashion production. These machines make it possible to cut fabrics with great precision, creating pieces that conform to patterns and reduce waste. The ability to make complex and detailed cuts is particularly useful in the production of high-fashion garments, where precision is critical.
Another significant application is in the furniture industry. Indeed, cutting machines are used to cut fabrics for upholstered furniture and furniture components, curtains, carpets, and wall coverings. The ability to handle materials of different densities and thicknesses makes these machines ideal for the production of decorative and functional elements, ensuring clean, precise cuts that improve the quality and durability of final products.
In the automotive industry, on the other hand, cutting machines are used to produce car interiors, including seats, upholstery, floor mats and panels. Here, too, the precision of the cuts is crucial to ensure that the components fit the vehicles’ specifications perfectly. Similarly, the aerospace industry benefits from advanced cutting machines for the production of aircraft interiors, including seat covers, partition panels, and curtains. Being able to cut lightweight but strong materials, such as technical fabrics and composites, is essential to meet the stringent safety and performance specifications required in this industry.
In the field of sports equipment manufacturing, professional cutters are used to create components for sportswear, footwear, and various equipment (camping tents, sleeping bags, backpacks, etc.), predominantly made from technical materials that must be processed with precision and care for the final packaging of products that offer comfort, durability, and high performance.
Coming out of the textile field, cutting machines also find applications in other industries. In the medical sector, for example, they are used to produce medical devices and accessories, such as masks, gowns, bandages and other medical products. Precise cuts and the ability to work with sterile materials prove essential to ensure the safety and effectiveness required by products for medical use.
In art and design, cutting machines make it possible to create textile artworks and decorative installations. Artists and designers can take advantage of the precision and versatility of these machines to explore new forms and techniques, producing innovative and detailed works.
The advertising and exhibition industry also uses these machines to produce banners, billboards, displays, and other promotional materials. The ability to cut fabric and synthetic materials with precision helps create eye-catching, high-quality visual elements that attract attention and effectively communicate the desired message.
Buying guide: tips for making the best choice
Purchasing a textile cutting machine requires a thorough assessment of one’s needs, considering intended use, type of fabric, accuracy, speed, ease of use and maintenance, and available budget. Taking all these factors into consideration will help you make an informed choice and invest resources in a machine that meets the specific needs of your textile business.
In order to best guide you, given the huge range of offerings on the market, we recommend that you contact a reputable and experienced manufacturer or dealer in the industry. This way you will be able to receive proper advice and all the assistance you need in choosing the textile cutting machine best suited to your needs and business goals.
In this regard, we at Fitex have specialized in the trade and production of spare parts, mechanical parts, accessories and complex solutions for the textile industry for over 40 years.
With more than 50 thousand items in our catalog, you can choose from a wide range of textile cutting machines of the best brands, which can guarantee a clean, accurate and neat cut on all types of material, with impeccable results every time.
Fitex guarantees you fast delivery, advanced technical advice and total support at all stages, from model selection to after-sales.
Contact us directly to request the ergonomic sewing chair model you are looking for and to receive a personalized quote and dedicated support.
Andrea Ferroli
Nadia Leonarduzzi
Order Directly with the Fitex App
Already know which item you need?
Order it directly from our app, available for Android and iOS.